4.5.9.11. CityJSON options¶
Note
These preference settings only apply to CityJSON exports.
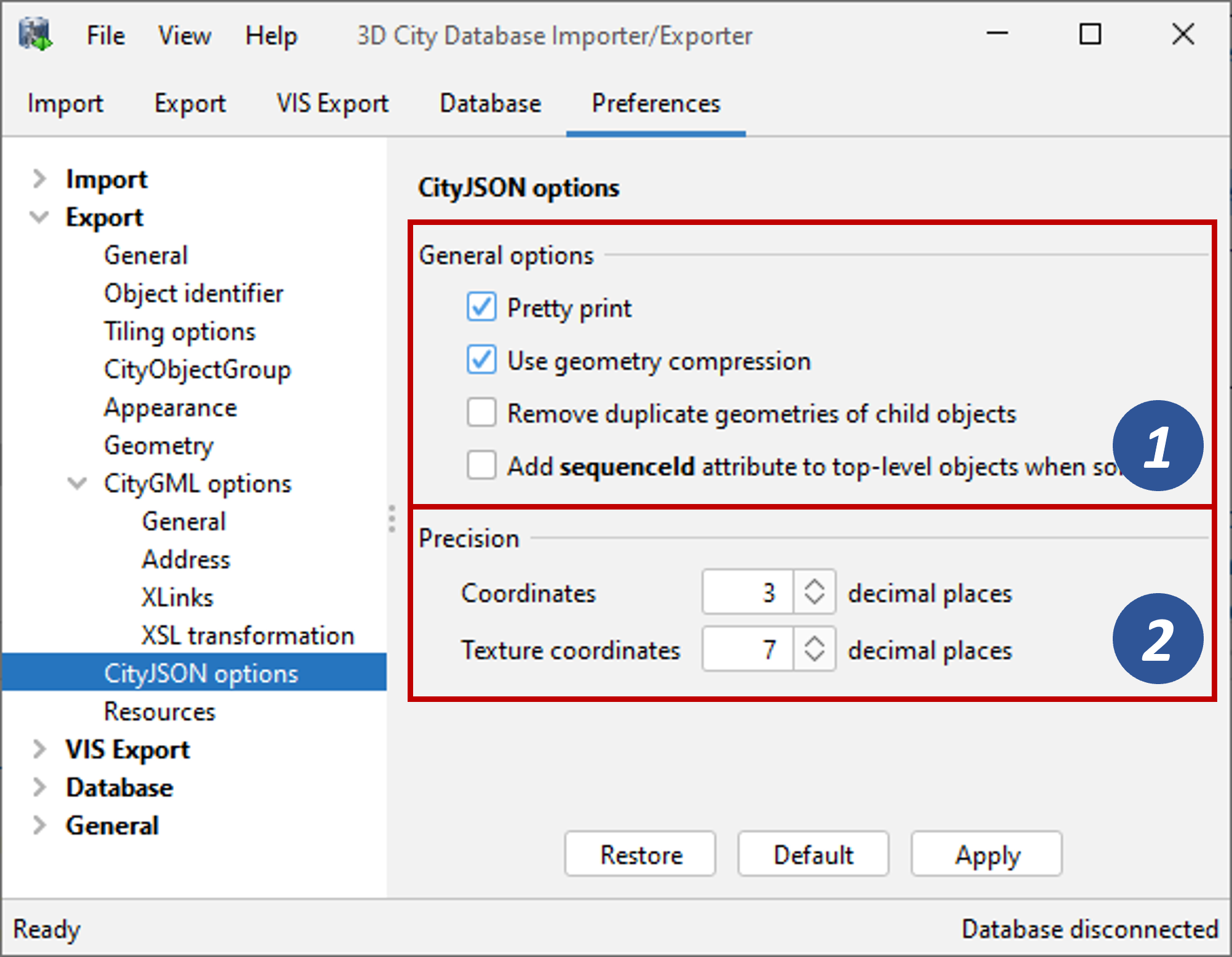
Fig. 4.50 Export preferences – CityJSON options.
General options
For CityJSON exports, the preference settings shown in Fig. 4.50 allow the user to enable pretty printing for the output file (default: disabled). When enabled, indentation is used for the JSON document and JSON elements are put on a new line. Without pretty printing, the entire data is put on a single long line. The file size will be considerably smaller without pretty printing, but the content is difficult to visually comprehend.
To reduce the file size, CityJSON also offers a way to compress the geometry by representing the coordinates of vertices with integer values rather than doubles (also called quantization). The scale factor and the translation needed to obtain the original coordinates are also stored in the file. Simply enable the Use geometry compression option to apply this compression method (enabled by default).
In CityGML, geometries can be reused using XLink references in order
to avoid duplicate geometries. For example, assume a building with a dormer.
The bldg:Building object in CityGML could be modelled such that
its geometry (gml:Solid or gml:MultiSurface) also contains
the shape of the dormer. In addition, the dormer itself can be modelled as
separate bldg:BuildingInstallation child object of the building with its
own geometry, which would reference those polygons from the building’s geometry that describe
the shape of the dormer.
CityJSON does not support reusing or referencing geometries.
When exporting the above example as CityJSON, the "BuildingInstallation" would
therefore also have its own geometry, but since the polygons from the "Building"
object cannot be referenced, this geometry would be duplicate. To avoid issues
with duplicate geometries in applications consuming the data, you can
activate the Remove duplicate geometries of child objects option.
Note
If the child object does not have any remaining geometry after removing the duplicate polygons, the entire child object will be removed as well.
Another general option available for CityJSON exports is to add a special
attribute of name "sequenceId" to every top-level city object when sorting
is enabled for the export (see Section 4.5.8.4). In a CityJSON file,
all city objects are stored as "CityObjects" collection.
This collection, however, is an unordered set and thus cannot be guaranteed
to reflect the result of the sorting operation. The "sequenceId" therefore adds
this information by storing the index of the city object in the sorted result set.
Note
The "sequenceId" uses zero-based numbering. Thus, the first top-level object
according to the sorting criteria is assigned the index 0, rather than the index 1.
Precision
For both the coordinates of vertices and texture coordinates, you can define the number of decimal places that should be kept in the output file. If the number of decimal places is greater in the database, the coordinates values are rounded accordingly during export. This helps to reduce the size of the resulting output file. The default behaviour is to keep 3 decimal places for vertex coordinates and 7 decimal places for texture coordinates.
Caution
A side-effect of rounding coordinate values is that two very close but distinct vertices in the database might receive the same coordinate values in the CityJSON file. If these two vertices are, for instance, consecutive points on the ring of a polygon, the Importer/Exporter will not remove one or the other from the ring. Thus, the exported polygon will contain duplicate consecutive points.